Cypher
Your secure password manager for all needs.
Welcome to Cypher
Globally deployed at cypher.harshiyer.me
Follow these slides at slides.harshiyer.me
Why Use a Password Manager?
Benefits of Password Managers
- Security: Avoid reusing passwords
- Convenience: Remember 2 strong passwords to get all others
- Cross platform password access
Why Cypher?
Cypher's Unique Features
- Open Source
- Client-Side Only
- High Security
- User-Friendly
- Cross-Device Compatibility
Tech Stack
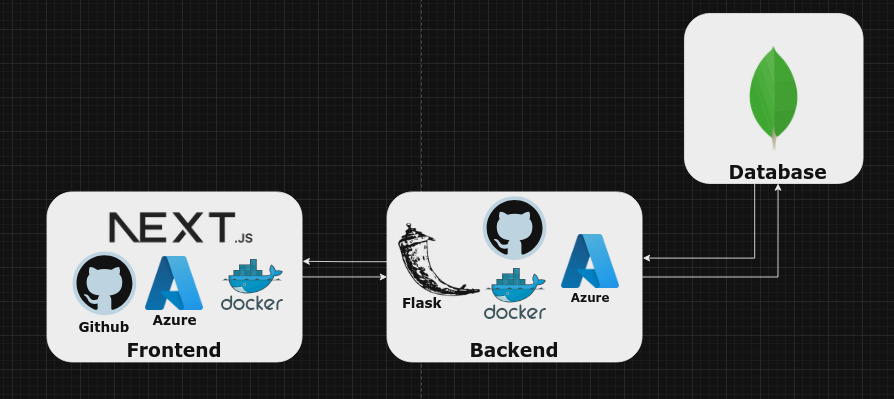
Quick Demo
cypher.harshiyer.me
How Cypher Works
Key Terminologies
Hashing Methods
Asymmetric Hash Function: Irreversible hash functions like SHA-256 are used to convert data into unique hashed values.
function hash(string) {
return createHash("sha256").update(string).digest("hex");
}
Hashing Example
Let's see an example for a famous one way hashing function: md5
function md5(string) {
return createHash("sha256").update(string).digest("hex");
}
console.log(md5("Cypher"))
// Output: 31edd1e8359d849e250b854826b8c387
AES: Encryption & Decryption
Why do we need AES?
AES is famously known for its two way encryption and decryption using one key as the factor for encryption and is very secure, which is all we need.
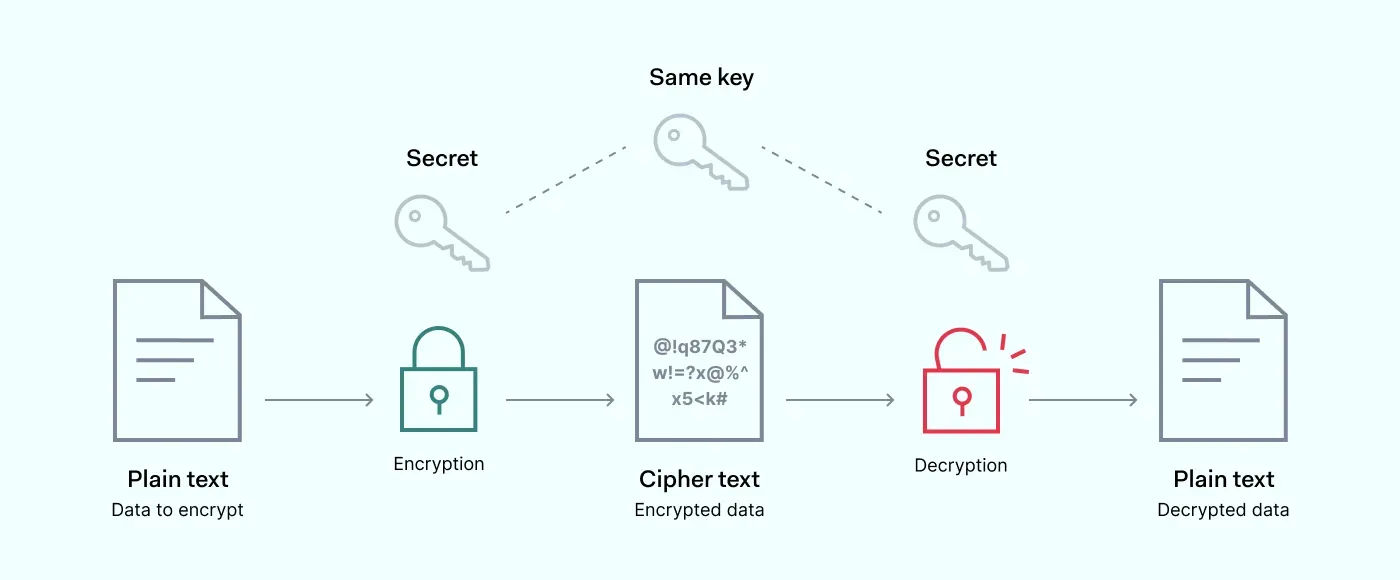
Symmetric Encryption (AES)
Symmetric encryption uses the same key for encryption and decryption. AES-256 is a widely used standard.
const {convertToAES} = require("@harshiyer/json-crypto");
const encryptedAESObject = await convertToAES(
{/*Data*/},
masterPassword
);
Decryption (AES)
The key(masterPassword) and salt ensure only authorized access.
const {convertFromAES} = require("@harshiyer/json-crypto");
const decrypted = convertFromAES(
aesString,
masterPassword,
salt
);
PBKDF2: Key Derivation
PBKDF2 derives a secure key from the master password by iterating hashing to a fixed bit size used for AES encryption.
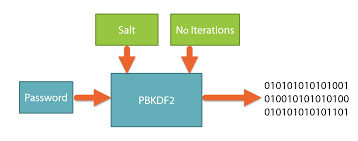
Libraries Used
- crypto
- @harshiyer/json-crypto
Data Flow
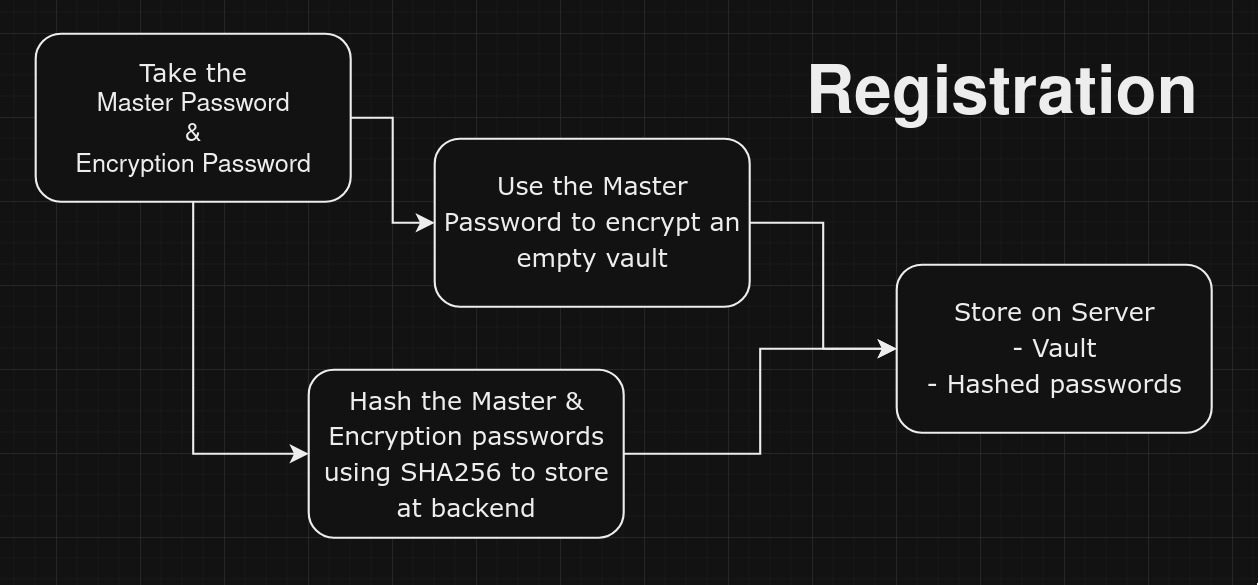
@app.route('/register', methods=['POST'])
@cross_origin()
def register():
data = request.json
username = data.get("username")
master_password = data.get("master_password") # Hashed version of the master_password
encryption_password = data.get("encryption_password") # Hashed version of the encryption_password
email = data.get("email")
# vault is an object with aes256 and salt in it
vault = data.get("vault")
aesString = vault.get("aesString")
salt = vault.get("salt")
# Check for required fields
if not username or not master_password or not encryption_password or not email:
return jsonify({"error": "Username, password, and email are required"}), 400
if username.strip()== "" or master_password == "" or encryption_password == "" or email == "":
return jsonify({"error": "Username, password, and email cannot be empty"}), 400
# Check if user already exists
if users_collection.find_one({"username": username}):
return jsonify({"error": "User already exists"}), 409
# Insert user data into MongoDB
users_collection.insert_one({
"username": username,
"master_password": master_password,
"encryption_password": encryption_password,
"email": email,
"aesString": aesString,
"salt":salt,
})
return jsonify({"message": "User created successfully"}), 201
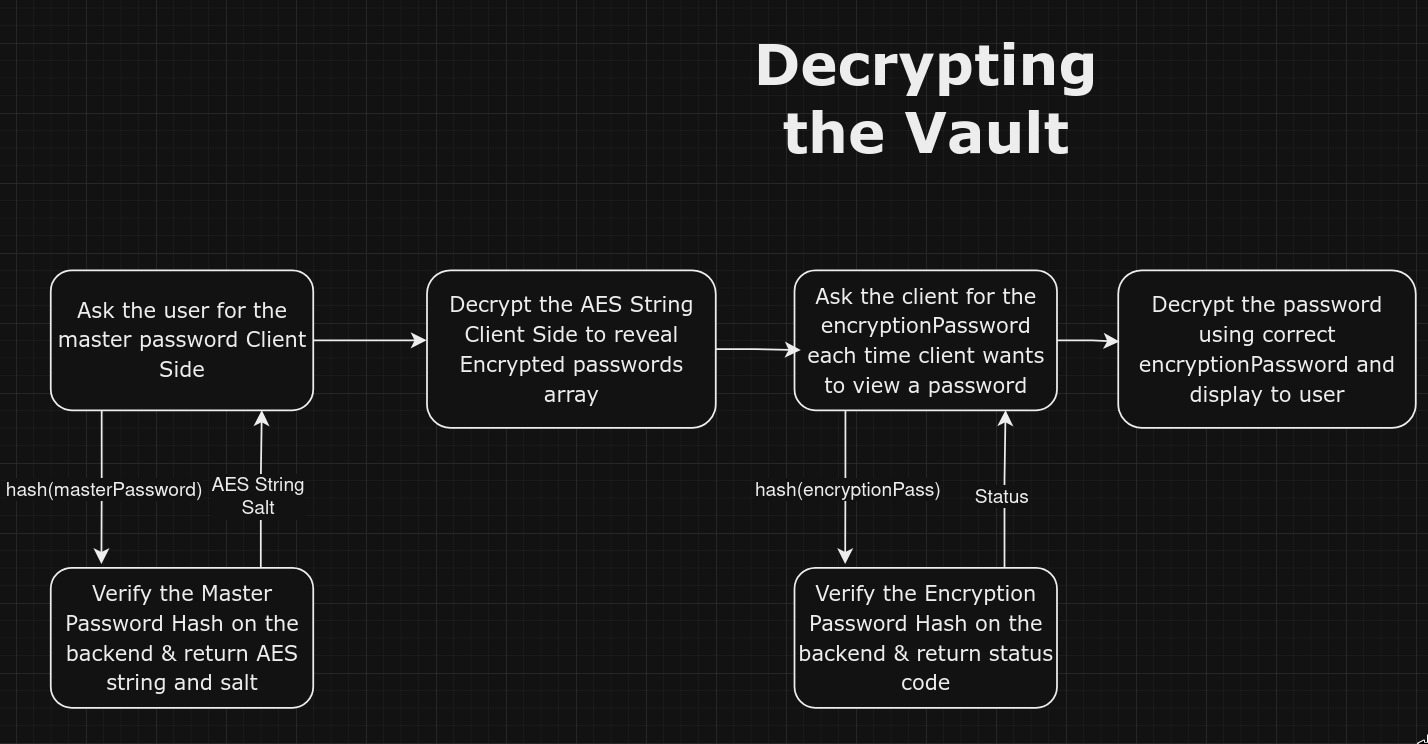
/* All this is happening Client Side */
const handleDecrypt = async () => {
try {
// Hash encryption password
const hashedPassword = await createHash("sha256")
.update(encryptionPassword)
.digest("hex");
// Verify encryption password with API
const response = await axios.post(`${apiURL}/verifyEncryptionPassword`, {
encryption_password: hashedPassword,
token: getCookie("token"),
});
if (response.status === 200) {
// Backend returns 200 if the password is correct
if (selectedPassword) {
// Attempt decryption
const decryptedPassword = convertFromAES(
selectedPassword.password,
encryptionPassword,
selectedPassword.salt,
);
console.log(decryptedPassword);
}
}
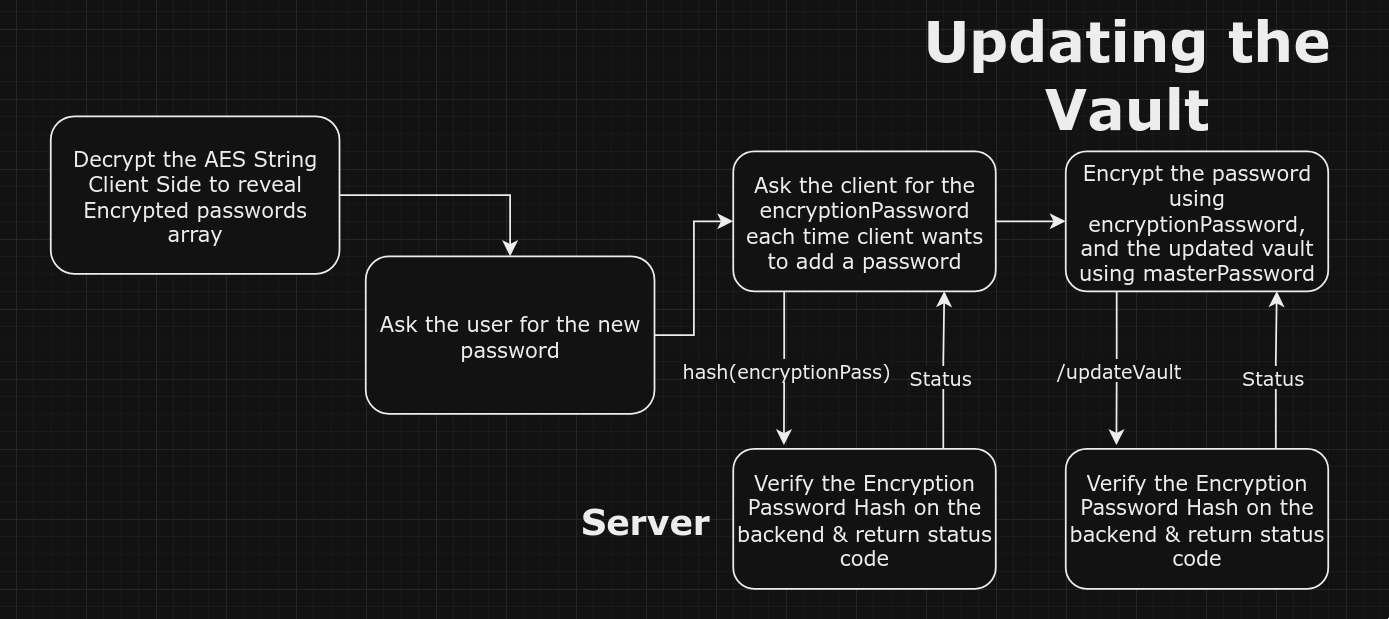
/* All this is happening Client Side */
const handleEncryptAndSave = async () => {
setLoading(true);
try {
await axios
.post(`${apiURL}/verifyEncryptionPassword`, {
encryption_password: await createHash("sha256")
.update(encryptionPassword)
.digest("hex"),
token: getCookie("token"),
})
.then((response) => {
console.log(response);
if (response.status == 201) {
toast({
title: "Password Verified Successfully!",
});
}
});
} catch (e: any) {
console.log(e);
if (e.response.status == 401) {
toast({
variant: "destructive",
title: "Incorrect Encryption Password!",
});
}
return;
}
const encryptedAESPassword = convertToAES(
newPassword.password,
encryptionPassword,
);
console.log(encryptedAESPassword);
if (encryptionPassword) {
const newEntry = {
id: passwords.length + 1,
...newPassword,
password: encryptedAESPassword.aesString,
salt: encryptedAESPassword.salt,
};
const updatedPasswords = [...passwords, newEntry];
setPasswords(updatedPasswords);
try {
const newAesObject = await convertToAES(
{ passwords: updatedPasswords, username: username },
masterPassword,
);
setNewAesString(newAesObject);
const token = getCookie("token");
const response = await axios.post(`${apiURL}/updateVault`, {
username: username,
aesString: newAesObject.aesString,
salt: newAesObject.salt,
token: token,
});
if (response.status === 201) {
toast({ title: "Updated successfully" });
}
} catch (e: any) {
console.error(e);
toast({
variant: "destructive",
title:
e.response?.status === 400
? "Account already exists!"
: "An error occurred!",
});
}
setNewPassword({ name: "", username: "", password: "", salt: "" });
setEncryptionPassword("");
/*Correctly updated at the backend*/
} else {
toast({
variant: "destructive",
title: "Please enter your encryption password!",
});
}
};
/* All this is happening Client Side */
const handleDelete = async () => {
if (passwordToDelete === null) return;
try {
// Filter out the password entry to delete
const updatedPasswords = passwords.filter(
(password) => password.id !== passwordToDelete,
);
setPasswords(updatedPasswords);
// Encrypt the updated passwords list
const newAesObject = await convertToAES(
{ passwords: updatedPasswords, username: username },
masterPassword,
);
setNewAesString(newAesObject);
// Send the updated vault data to the server
const token = getCookie("token");
const response = await axios.post(`${apiURL}/updateVault`, {
username: username,
aesString: newAesObject.aesString,
salt: newAesObject.salt,
token: token,
});
if (response.status === 200) {
/*Password is deleted successfully*/
}
} catch (e: any) {
console.error(e);
/*Handle error gracefully*/
} finally {
setShowDeleteDialog(false); // Close dialog after deletion
setPasswordToDelete(null); // Reset state
}
};
Key Takeaways
- Even if the entire database gets leaked, no one can decrypt your passwords without having BOTH the Master and Encryption Key.
- Even if the server gets compromised, the data is safe because it is encrypted using a password only the client knows.
- If someone finds your masterPassword, they still cant see your passwords thanks to 2 level encryption.
- Remember 2 passwords, leave the rest to us.
Future Scope
Web Extension
Developing a browser extension for saving and getting passwords on the go.
Biometric Authentication
Implementing biometric authentication for enhanced security.
Two-Factor Authentication
Adding 2FA for additional security.